Google PSA: Removing HTTP Version of Site Will Remove All Versions

LinkedIn got itself deindexed from Google list items on Wednesday, which might possibly have happened because of a blunder on their part.
The indication of a whole space being deindexed from Google is playing out a “site:” search and seeing zero outcomes.
That was actually the situation with LinkedIn prior today:
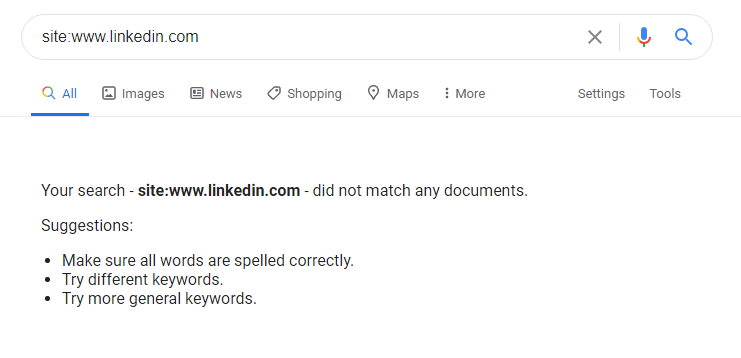 There were no outcomes for LinkedIn in Google from early morning to mid evening on Wednesday – about 10 hours altogether.
There were no outcomes for LinkedIn in Google from early morning to mid evening on Wednesday – about 10 hours altogether.
There’s no uncertainty this significantly affected LinkedIn’s traffic for the afternoon, yet the site itself was as yet open.
Clients could in any case visit LinkedIn by exploring to the area legitimately, or by tapping on joins somewhere else on the web.
All things considered – the site was not down, it was simply de-filed from Google.
How Did This Happen?
The subject of the day is how did this wind up occurring in any case?
Neither LinkedIn or Google have formally remarked regarding the matter at the hour of this composition.
Notwithstanding, there are several potential clarifications.
LinkedIn May Have Removed HTTP Version of Site
John Mueller distributed a tweet toward the beginning of today which may have been in a roundabout way focused on LinkedIn.
PSA: Removing the “http://” rendition of your site will evacuate all varieties (http/https/www/non-www). Try not to utilize the evacuation apparatuses for canonicalization.https://t.co/yTfRzWZGtd
— 🍌 John 🍌 (@JohnMu) May 6, 2020
It’s conceivable LinkedIn incidentally expelled itself from Google’s record by evacuating the HTTP rendition of its site in Search Console.
On the off chance that that is the situation, which has not been affirmed, LinkedIn may have done as such with an end goal to canonicalize the HTTPS rendition of its site.
Mueller unequivocally states: “Don’t utilize the evacuation instruments for canonicalization.”
LinkedIn Disallowed Crawling Via Robots.txt?
As indicated by proof found while LinkedIn was de-filed, it’s clear Google’s crawlers were hindered with a robots.txt order.
Truly astounding that @LinkedIn has blocked themselves from Google.
Miracle on the off chance that they additionally evacuated themselves by means of GSC to get this a lot of a total separation!
h/t @IanLurie pic.twitter.com/r02yH1qS5R
— lorenbaker (@lorenbaker) May 6, 2020
Obstructing Google’s crawlers is a certain method to get de-listed too. Be that as it may, the effect generally isn’t as prompt as it was for LinkedIn’s situation.
As expressed by Loren Baker in the tweet over, this a lot of a “total separation” from Google’s record is bound to be identified with a Google Search Console expulsion.
Related: 9 Ways to Deindex Pages from Google
LinkedIn is Back in Google Search Results
Whatever the issue may have been, it has since been amended as LinkedIn has come back to Google’s indexed lists.
In the case of nothing else, let this be an exercise that even a portion of the web’s greatest destinations commit errors occasionally.
This can likewise fill in as an exercise that Google doesn’t fix botches all alone.
Never accept that Google is sufficiently keen to recognize these things and fix them before they transform into a significant issue.
Exercise learned: never expect Google is savvy enough to do anything.
— Dustin Woodard (@webconnoisseur) May 6, 2020
Have confidence the SEO people group won’t let LinkedIn live this one down at any point in the near future.
I’ll bet that, for quite a long time to come, we’ll be referencing the time LinkedIn de-filed itself from Google.